Instructions: Click on the button to see if your answer is correct or not. I recommend keeping track of how many you get correct on your first try. There are 120 questions, which equals about 0.833 points each. You might need your reference tables for this... look in the back of your book, starting on page 265.
A student broke a mineral sample with a tap of a hammer on a sharp chisel. What property was she investigating?
Specific gravity
Cleavage
Luster
Streak
How can you determine the hardness of a mineral?
Use it to scratch other solid materials.
Crush it in a vice.
Drop it onto a concrete surface.
Drop it into a graduated cylinder half-full of water.
Many mineral samples are composed of:
rocks.
ice.
crystals.
plastics.
Which of these mineral characteristics would not be useful in identifying a mineral sample?
Volume
Density
Luster
Streak
Which mineral property depends upon how light is reflected from a fresh mineral surface?
Specific gravity
Cleavage
Luster
Streak
The screwdriver is pushing the layers apart.

What mineral property is shown being tested in the diagram below?
Specific gravity
Cleavage
Luster
Streak
Which property of quartz is the most likely to change the most, over a wide variety of quartz samples, due to minor impurities?
Hardness
Luster
Density
Color
Which of the following terms best describes a surface that reflects almost all of the light that hits it?
Metallic
Waxy
Opaque
Dark
Which of the following mineral properties is something you cannot see just by looking at a mineral sample?
Hardness
Crystal form
Color
Luster
If no light can pass through a mineral, and you cannot see through it, it is said to be:
luster.
translucent.
transparent.
opaque.
If light can pass through a mineral, and you can see through it, it is said to be:
luster.
translucent.
transparent.
opaque.
If most light can pass through a mineral, and you cannot see through it, it is said to be:
luster.
translucent.
transparent.
opaque.
Which property of quartz is always the same from sample to sample?
Hardness
Size
Mass
Color
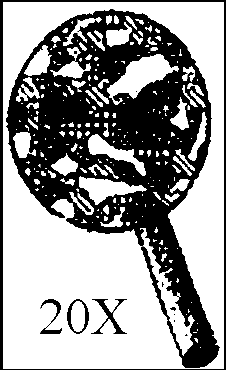
![]()
Base your answers to questions 14 and 15 on the
diagram below shows the results of one test for mineral identification.
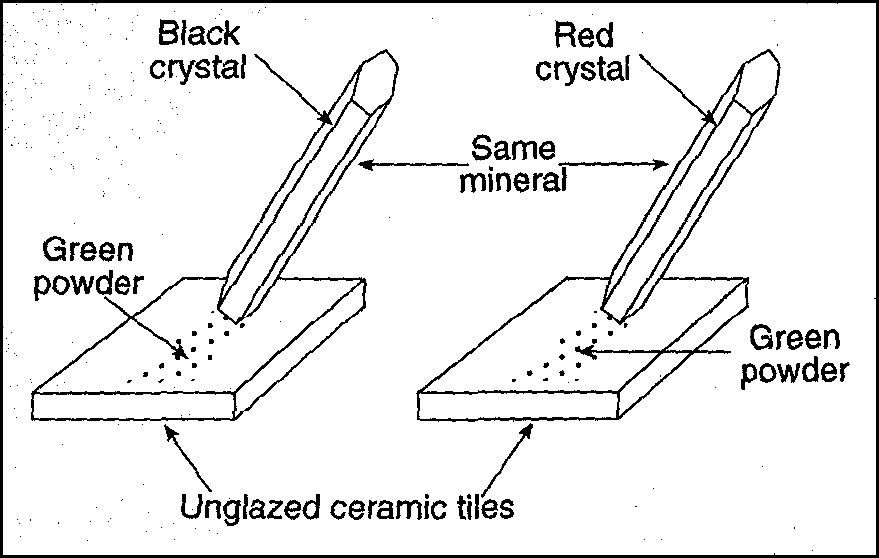
Which mineral property is being tested?
density
streak
fracture
luster
If both of these minerals are two different samples of the same mineral, what is the minerals REAL color and why do they look different?
The real color is red black, the second one looks red due to impurities in the mineral, and the green powdery line left behind does not matter.
The real color is red, the first one looks black due to impurities in the mineral, and the green powdery line left behind does not matter.
The real color is green, the first one looks black and the second one looks red due to different impurities in each of the mineral.
The real color is red or black, but the powder left behind for both samples looks green due to impurities in the mineral.
![]()
Which of the following elements is not found in Plagioclase Feldspar?
Aluminum
Lead
Silicon
Sodium
A student is trying to identify a mineral sample. She notices that it reflected very little light, and did not look like metal. The mineral scratches fluorite, but is scratched by quartz. When she taped it with a hammer, it split naturally in two directions (both at 90º), and when she rubbed the mineral against an unglazed porcelain plate, it left a very dark green powder behind. Which mineral is she looking at?
Amphiboles
Olivine
Potassium feldspar
Pyroxene
A mineral's crystal shape and cleavage are a direct result of the mineral's
exposure to the hydrosphere and atmosphere.
internal arrangement of atoms.
abundance in nature.
hardness.
Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5 on the Moh's scale, and splits with cubic cleavage?
calcite
pyrite
halite
mica
![]()
Base your answers to questions 25 through 27 on on the
diagram below, which shows three minerals with three different physical
tests, A, B, and
C, being performed on them.
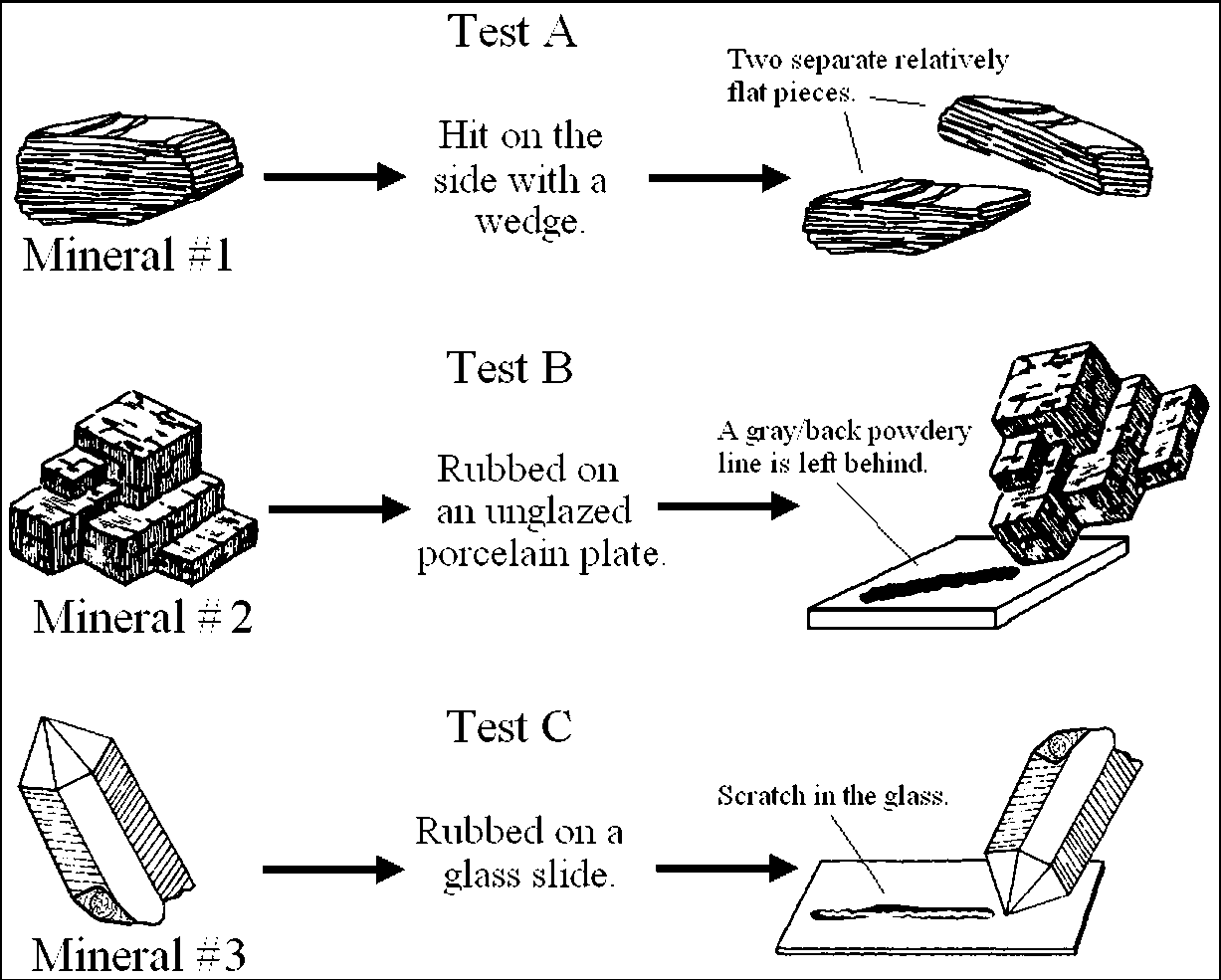
Why would these minerals have the properties shown here?
The minerals have these properties because these are the
only minerals that demonstrate cleavage, hardness, and streak.
The minerals have these properties because of the internal arrangement of atoms within the mineral.
The minerals have these properties because of the color, luster, and translucency of the minerals.
The minerals have these properties because all minerals easily split into two relatively flat pieces when struck with a wedge, leave a gray/black streak, and can scratch glass.
The results of all three physical tests shown above are most useful for determining the
rate of weathering of the minerals.
environment where the minerals formed.
identity of the minerals.
geologic period when the minerals formed.
Which sequence correctly matches each test, A, B, and C, with the mineral property tested?
A = streak; B = hardness; C = cleavage
A = cleavage; B = hardness; C = streak
A = cleavage; B = streak; C = hardness
A = streak; B = cleavage; C = hardness
![]()
Two minerals made of pure carbon are diamond and graphite. Which statement best explains why diamond is so much more resistant to scratching than graphite?
The atoms are bonded together more strongly in diamond than in graphite.
The atoms are smaller in graphite than in diamond.
The atoms are lighter in graphite than in diamond.
The atoms are heavier in graphite than in diamond.
Which mineral scratches dolomite and is scratched by
olivine?
potassium feldspar
muscovite mica
quartz
galena
Which mineral scratches fluorite, is scratched by olivine, has a non-metallic luster, cleaves at two directions at 90°, and is black to dark green in color?
Amphiboles
Potassium feldspar
Pyroxene
Plagioclase feldspar
What element is in Dolomite, but not Calcite?
Aluminum
Carbon
Calcium
Magnesium
According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, rhyolite is an example of a
monomineralic igneous rock
polymineralic igneous rock
monomineralic sedimentary rock
polymineralic sedimentary rock
Which rock type is most likely to be monomineralic?
rock salt
basalt
rhyolite
conglomerate
Which statement is supported by information in the Rock Cycle diagram in the Earth Science Reference Tables?
Metamorphic rock results directly from melting and crystallization.
Sedimentary rock can only be formed from igneous rock.
Igneous rock always results from melting and solidification.
All sediments turn directly into sedimentary rock.
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks are usually
composed of
intergrown crystals
fossils
minerals
sediment
Rocks can be classified as sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic based primarily upon differences in their
color
origin
density
age
Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of
white quartz
aluminum
potassium feldspar
iron
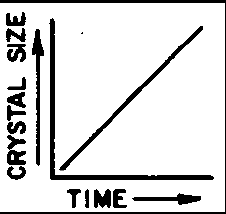
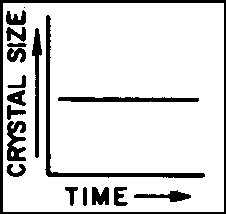
Which graph best shows the relationship between the size of the crystals in an igneous rock and the length of time it has taken the rock to solidify?
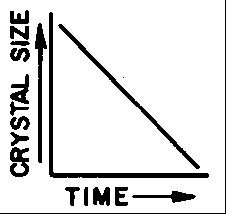
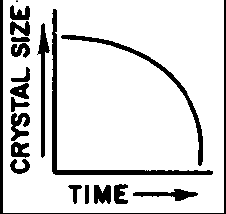
Which granite sample most likely formed from magma that cooled and solidified at the slowest rate?
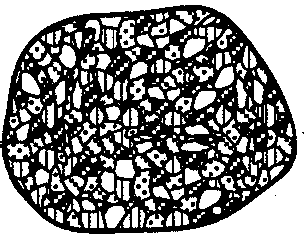
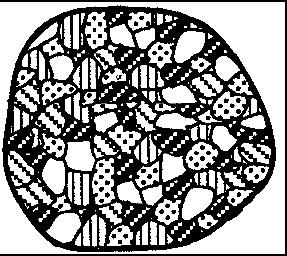
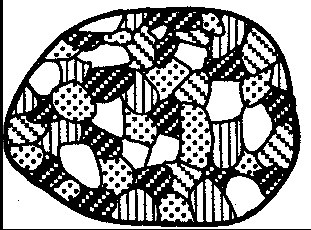
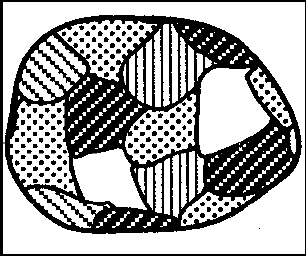
The diagrams below represent four different rock samples. Which rock took the longest time to solidify deep within the Earth?
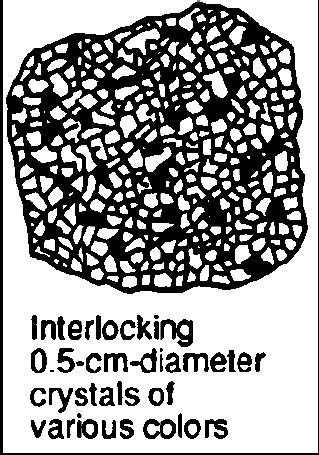
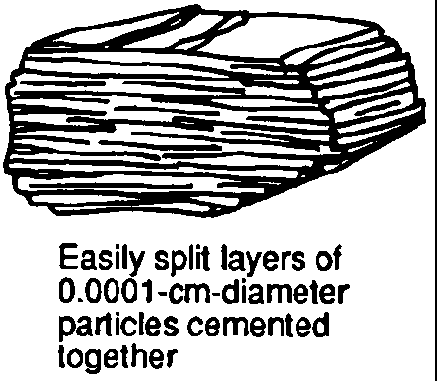


Some Moon rock samples have coarse intergrown crystals composed of plagioclase feldspar, hornblende, and olivine. These Moon rock samples are most similar to Earth rock samples of
breccia
gabbro
marble
pumice
According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, rhyolite and granite are alike in that they both are
fine-grained
dark-colored
mafic
felsic
Which property is common to most dark-colored igneous rocks?
high density
intrusive formation
abundant felsic minerals
coarse-grained textures
Which two terms mean EXACTLY the same thing?
Intrusive and Extrusive
Volcanic and Plutonic
Extrusive and Volcanic
Extrusive and Plutonic
Choose the choice that best fill in the blanks "X" and "Y."
In igneous rocks, the
(X) the
rock cools, the
(Y) its
crystals will be.
(X) faster (Y) flatter
(X) slower (Y) larger
(X) slower (Y) smaller
(X) faster (Y) larger
Which of the following is an example of an igneous rock?
Calcite
Shale
Slate
Granite
Igneous rock that is iron (Fe) and Magnesium (Mg) rich, tends to be darker in color and more dense than feldspar and quartz (SiO2) rich rocks are called:
foliated
non-foliated
mafic
felsic
The diagrams below show the crystals of four different rocks viewed through the same hand lens. Which crystals most likely formed from molten material that cooled and solidified the quickest?

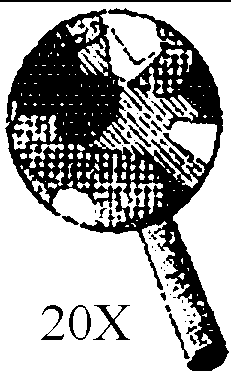

One similarity between a sand pile and sandstone is that they
are composed of sediments
always contain fossils
contain a cementing agent
have a crystalline structure
According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, particles of which size could have formed shale?
0.2 cm
0.02 cm
0.002 cm
0.0002 cm
Which characteristic is most common in sedimentary rocks?
foliation
layering
intergrown crystals
glassy texture
![]()
Base. your answers to questions 47 and 48 on the formation of

which sedimentary rock is shown in the diagram?
conglomerate
sandstone
siltstone
shale
Which two processes formed this rock?
folding and faulting
melting and solidification
compacting and cementation
heating and application of pressure
![]()
According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, which rock most likely formed as a result of biologic processes?
granite
basalt
sandstone
limestone
Which of the following is an example of an sedimentary rock?
Calcite
Shale
Slate
Granite
Which of the following is an example of an metamorphic rock?
Calcite
Shale
Slate
Granite
A clastic sedimentary rock that has many different grain sizes, from clay-sized to gravel-sized, “cemented” together, where the majority of the fragments are angular in shape is
basalt
metaconglomerate
conglomerate
breccia
Which sedimentary rock is most likely to be changed to slate during regional metamorphism?
breccia
conglomerate
dolostone
shale
Which sample best shows the physical properties normally associated with regional metamorphism?




In which rock might you find a fossil?
Limestone
Granite
Gneiss
Slate
Which rocks are formed by the solidification of hot molten rock material called magma?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Minerals
Which rocks are formed from sediments being cemented or bound together in some way?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Minerals
Which rocks are formed by the effects of heat, pressure, and (sometimes, but rarely) chemical actions on other rocks?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Minerals
The terms clastic (or fragmental), crystalline (or chemical), and bioclastic (or biochemical) are used to describe types of:
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Minerals
![]()
Base your answers to questions 60 through 62 on the series of rocks in the image below and their descriptions.

Which rock is metamorphic and shows evidence of foliation?
1
2
3
4
What do all four rock samples have in common?
The are organically formed.
They show cleavage.
The formed on the Earth's surface.
They contain minerals.
Which of the following is sedimentary?
1
2
3
4
![]()
What is the best way to test the hardness of a mineral?
Measure the mass and volume of the sample.
Squeeze the mineral with calibrated pliers.
Break the mineral by hitting it with a hammer.
Use the mineral to scratch a glass plate.
An unidentified mineral that is softer than calcite exhibits a metallic luster and cubic cleavage. This mineral is most likely
pyroxene
pyrite
halite
galena
![]()
Base your answers to questions 65 and 66 on the geologic cross section below, which shows limestone that was intruded. Part of the limestone (zone A) was heated intensely but was not melted.
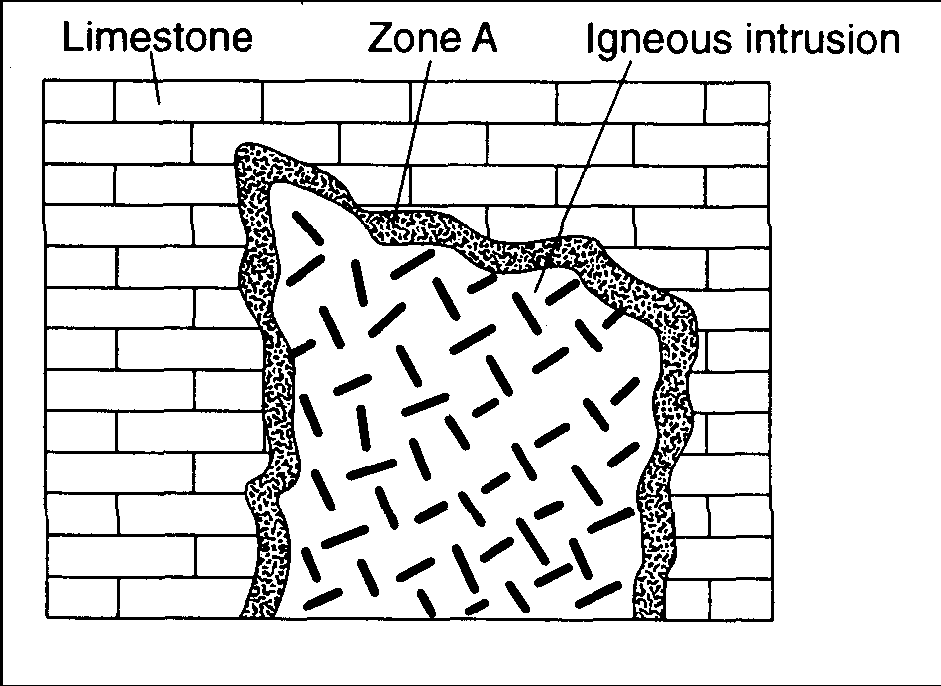
Which mineral is most abundant in Zone A?
Limestone
Quartz
Marble
Calcite
Which type of rock most likely formed in zone A?
slate
gneiss
marble
obsidian
![]()
The picture below shows the igneous rock obsidian.
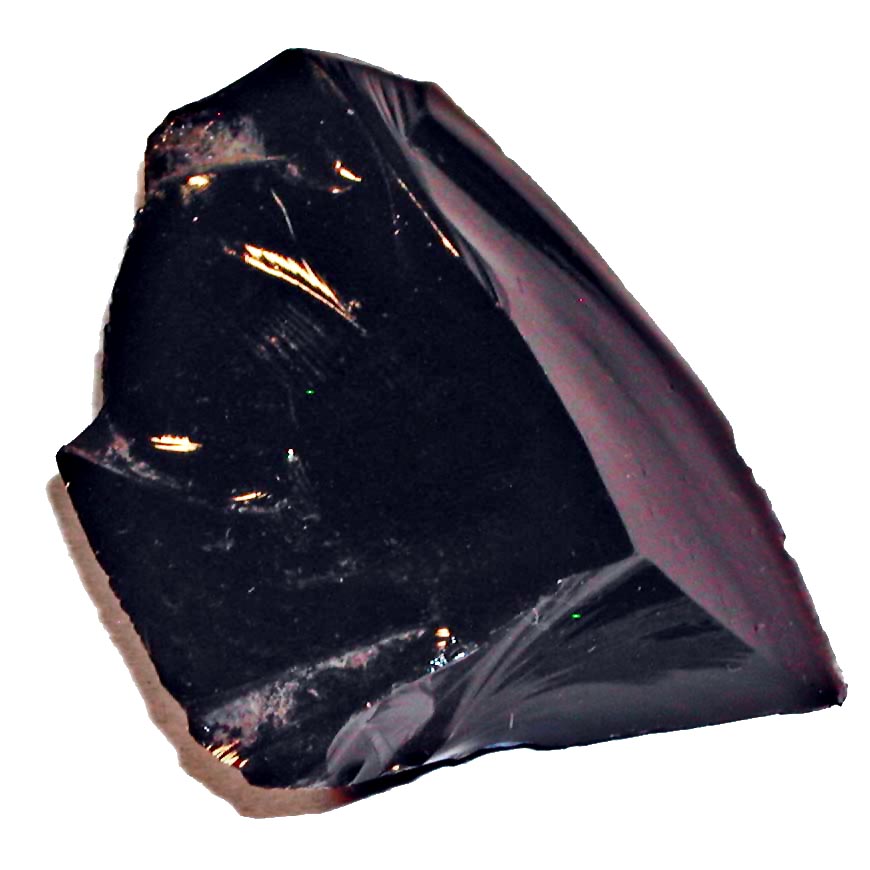

The obsidian's glassy texture indicates that it formed from a magma that cooled
quickly, on Earth's surface
quickly, deep below Earth's surface
slowly, on Earth's surface
slowly, deep below Earth's surface
The diagram below shows the mineral composition of an igneous rock drawn actual size.

According to the Earth Science Reference Tables, this igneous rock is
granite
rhyolite
basalt
gabbro
![]()
For questions 69 through 91, choose the proper rock type or rock types related to the clue given. Please note that it is possible for the clue to refer to more than one rock type at the same time. It may even refer to all three, or none at all.
What type of rock do you have if it is not a metamorphic rock?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it was transformed by heat and pressure?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it was formed by compression?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it has foliation?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it it is made up of other rocks that never completely melted?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it has quartz in it?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it was formed from partial melting and recrystallization?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it made up of shells?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it it was NOT formed directly from the cooling of magma or lava?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is vesicular?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is a rock that could be made up of both calcite and dolomite?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is a mafic rock with banding and a bioclastic texture?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it has mineral alignment?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it was formed through lithification?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it has banding?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is included in the rock cycle?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it has fossils?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it was formed by processes related to some amount of heat?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is either intrusive or extrusive?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it is made up of weathered materials?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it started as an igneous rock before it was affected by some process?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it started as an metamorphic rock before it was affected by some process?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
What type of rock do you have if it started as an sedimentary rock before it was affected by some process?
Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock
![]()
For questions 92 through 103, read the statement and determine if it is true or false. Please note that in order for an answer to be "True," the entire statement must be true. However, if the entire statement is not true, or any part of the statement is false, the answer will be "False."
Diamonds and Graphite are both made of the same element, Carbon (C), but they have differ in hardness due to differences in their internal molecular structures.
Hardness in measured on a scale from one to ten, called the Moh's hardness scale, where one is the hardest and ten is the softest.
The hardness of a mineral can be determined by scratching it against another solid substance.
Looking at the color of a mineral is the best way to identify it.
Cleavage is the term that we use to describe how well the mineral reflects light.
Many minerals are made up of rocks.
When a rock is completely melted, it can crystallize into a metamorphic rock.
A rock can be called a sandstone if it is made up of pieces of weathered sediment that are cemented together in some way, as long as the grain size is between 0.006 and 0.0004 cm.
You can tell a rock like granite was formed in an intrusive environment, because the majority of the crystals are less than 1 mm in size.
According to the rock cycle, any type of rock can become any type of rock. For example, a metamorphic rock can become a different metamorphic rock.
The deeper into the Earth the protolith is, more heat and pressure the rock experiences, and the higher the grade of metamorphism.
The higher the grade of metamorphism a rock experiences, the more difference between the new rock and its protolith.
![]()
For questions 104 through 120, please determine whether or not an object is a mineral.
Olivine
Graphite
Sulfur
Hydrogen
Lead
Water
Coral
Diamonds
Coal
Fossils
Plastic
Ice
"Dry Ice" (frozen CO2) on Earth.
"Dry Ice" (frozen CO2) in a comet.
Rose Quartz
Any naturally occurring, inorganic, solid substance with a definite chemical composition and distinct physical properties, such as mineral structure, cleavage, and hardness.
yes buttons