Chapter 4 Test Review
Instructions: Click on the button to see if your answer is correct or not. I recommend keeping track of how many you get correct on your first try. Then, multiply that number by 1.25, and you will have a grade out of 100 (80 questions are listed here). Also, watch your timing! These 80 questions should not take you longer than an hour.
Clay
Silt
Sand
Cobbles
Magma is composed of pebbles.
Any large rock that weathers could become a pebble.
Pebbles can become cemented together to form a rock called gabbro.
Smaller rocks can grow into bigger rocks.
The smooth, polished surface of a rock in a dry, sandy area.
Blocks of basalt at the base of a steep slope.
A pattern of parallel cracks in a granite mountain.
Large caves in limestone bedrock.
A dry climate which temperatures alternate from below freezing to above freezing.
A dry climate which temperatures remains below freezing.
A wet climate which temperatures alternate from below freezing to above freezing.
A wet climate which temperatures remains below freezing.
physical weathering.
chemical weathering.
erosion.
deposition.
lithosphere and atmosphere.
hydrosphere and atmosphere.
mesosphere and thermosphere.
hydrosphere and lithosphere.
Decreasing temperature and increasing precipitation.
Decreasing temperature and decreasing precipitation.
Increasing temperature and increasing precipitation.
Increasing temperature and decreasing precipitation.
10.0 g/min
4.0 g/min
2.0 g/min
0.5 g/min
When minerals are dissolved, how are the resulting ions carried by rivers?
in solution
in suspension
by tumbling and rolling
by precipitation
It will become jagged and its mass will decrease.
It will become jagged and its volume will increase.
It will become rounded and its mass will increase.
It will become rounded and its volume will decrease.
Cobbles
Pebbles
Sand
Silt
As the velocity of a stream decreases, the amount of sediment in the water of the stream
increases.
decreases.
stays the same.
Two 10-gram samples of limestone are dropped into 20 milliliters of diluted hydrochloric acid. One of the 10-gram samples had been ground into a fine powder. The most likely reason the powdered limestone reacts faster in the acid then the unbroken sample is that it has
less total volume.
more chemical bonds.
more total surface area.
lower density.
Earth's average temperature decreases.
Their rate of melting exceeds their rate of advancing.
They encounter the ocean.
The crust beneath them is uplifted.
At the top of a steep slope in a streambed.
At a site where glacial ice scrapes bedrock.
At the mouth of a river, where it enters an ocean.
On the side of a sand dune facing the winds.
slope of the landscape
longitude
amount of rounded sediment
climate
The chief agent of erosion on Earth is
wind.
glaciers.
human beings.
running water.
In which type of climates does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly?
Cool and arid.
Cool and humid.
Warm and arid.
Warm and humid.
Sediment, from the weathering of rock materials, and humus, which is formed by the decay of organic materials, are important for the formation of most
sediment.
surface bedrock.
soils.
minerals.
gneiss boulder was formed from sediments that were compacted and cemented together.
gneiss boulder was transported from its original area of formation.
surface sedimentary bedrock was weathered to form a boulder of gneiss.
surface sedimentary bedrock melted and solidified to form a boulder of gneiss.
waves.
wind.
a glacier.
a stream
![]()
Use the diagram below to answer questions 22 through 25. The diagram represents the landscape features associated with a meandering river using letters A, B, C, D, E, and F to represent these features and locations.

The diagram below represent 3 stages in the formation of a meandering river.
Which of the following sequences best represents the usual changes over time?
A -> B -> C
A -> C -> B
B -> C -> A
C -> B -> A
erosion on the inside curves of the meanders
weathering of the soil on the riverbanks
deposition when the river overflowed its banks
deposition by the yazoo stream.
a decrease in the slope of the river
a decrease in the temperature of the river
an increase in the river's discharge
an increase in the width of the river
erosion due to an increase in stream velocity.
erosion due to a decrease in stream velocity.
deposition due to a increase in stream velocity.
deposition due to a decrease in stream velocity.
![]()
The elevation of the entire region will increase.
The rate of wind erosion will increase.
The landscape features will become more rounded.
The limestone will stop dissolving.
The elevation of the entire region will decrease.
The rate of wind erosion will decrease.
The landscape features will become more angular.
The limestone will quickly dissolve.
The cracks become wider because of chemical reactions between the water and the rock.
This type of weathering is common in regions of primarily warm and humid climates.
Enlargement of the cracks occur because water expands when it freezes.
This type of weathering occurs only in bedrock composed of granite.
are horizontal .
have different compositions.
contain different fossils.
formed during different time periods.

How did the arch most likely form?
An earthquake forced bedrock upward into the shape of an arch.
The bedrock in the arch was more resistant to weathering and erosion than the surrounding bedrock that was removed.
An underground glacier tunneled through the bedrock.
Sand and gravel were deposited and compacted into the shape of an arch.

Which evidence suggests that ice created this landscape.
sorted sediment on the valley floor
the landslide near the valley
U-shaped valleys
many stream valleys
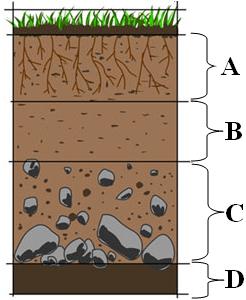
Which soil horizon contains the greatest amount of material formed by biological activity?
A
B
C
D
What was the primary force that causes landslides?
gravity
moving ice
prevailing winds
stream discharge
![]()
Base your answers to questions 34 through 40 on the map below. Letters A through F represent locations in the stream.
C and E
D and E
F and D
C and F
Which locations experience the greatest amount of deposition?
C and E
D and E
F and D
C and F
In which locations would the velocity of the water be the highest?
C and E
D and E
F and D
C and F
In which locations would the velocity of the water be the lowest?
C and E
D and E
F and D
C and F
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
![]()
Base your answers to questions 41 through 42 on the block diagram below, which shows some of the landscape features formed as the most recent continental glacier melted and retreated across western New York State
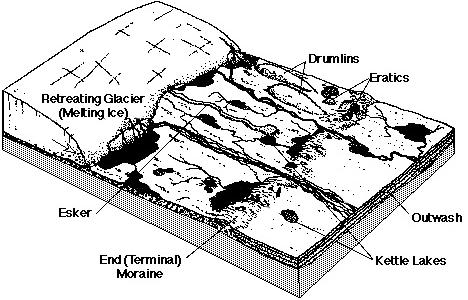
unsorted by size and stratified.
unsorted by size and unstratified.
sorted by size and stratified.
sorted by size and unstratified.
The shape of elongated hills labeled drumlins is most useful in determining the
thickness of the glacial ice.
rate of glacial movements.
age of the glacier.
direction of glacial movements.
![]()
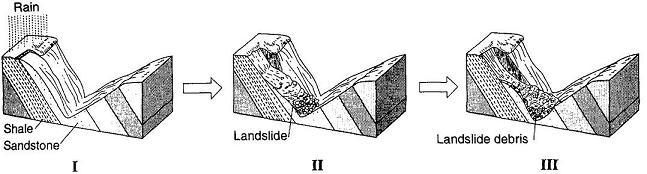
What was the primary force that caused this landslide?
Gravity
Prevailing winds
Moving ice
Stream discharge
In which general direction is the sand being moved along this shoreline by the longshore current?
northeast
northwest
southeast
southwest
On which map do the arrows best show the direction of wave movements that create the beaches in this area?
A
B
C
D
Use the cross section below to answer questions 46 and 47, which illustrates the general sorting of sediment by a river as it flows from a mountain to a plain.
velocity of the river
hardness of the surface bedrock
mineral composition of the sediment
temperature of the water
What type of sorting is shown in this cross section?
Unsorted
Horizontal sorting
Vertical sorting
Diagonal sorting
What is the probable relationship between erosion and deposition at points A and B after the earthquake?
There is more deposition at point A and more erosion at point B.
There is more erosion at point A and more deposition at point B.
There is more deposition than erosion at points A and B.
There is more erosion than deposition at points A and B.
type of bedrock
amount of folding
time
climate.
Particles that are small in size, have a low density, are flat in shape, and have a rough texture.
Particles that are large in size, have a low density, are round in shape, and have a rough texture.
Particles that are large in size, have a high density, are flat in shape, and have a smooth texture.
Particles that are large in size, have a high density, are round in shape, and have a smooth texture.
precipitation.
runoff.
infiltration.
snow melt.
As the particle size increases, the permeability rate increases.
As the particle size decreases, the permeability rate decreases.
As the particle size decreases, the permeability rate increases.
As the particle size increases, the permeability rate decreases.
poorly sorted and densely packed.
well sorted and densely packed.
poorly sorted and loosely packed.
well sorted and loosely packed.
The upward movement of water through tiny spaces in soil or rock is called
water retention.
porosity.
capillary action.
permeability.
Folded Motion and Arrow Motion
From Media and About Media
Frequency Modulation and Amplitude Modulation
Future Music and Antiquated Music
clay
sand
silt
pebbles
saturated soil
coarse-grained soil
a steep soil surface
an impermeable surface
capillarity
runoff
infiltration into the ground
the level of the local water table
sand
clay
silt
pebbles
saturated and permeable.
saturated and impermeable.
unsaturated and permeable.
unsaturated and impermeable.
different sizes and shapes.
small and rounded.
large and angular.
large and rounded.
infiltration
capillarity
porosity
permeability rate
The combination of iron with oxygen to form rust.
The dissolving of the mineral halite into is ions by hydration.
The wearing away of shale by wind-blown sand.
The dissolving of limestone by carbonic acid.
increase.
decrease.
remain the same.
rapidly decrease before it starts to increase.
The rate of chemical weathering is lower in smaller particles, because they have more surface area than a larger particle.
The rate of chemical weathering is lower in smaller particles, because they have less surface area than a larger particle.
The rate of chemical weathering is higher in smaller particles, because they have more surface area than a larger particle.
The rate of chemical weathering is higher in smaller particles, because they have less surface area than a larger particle.
Water dissolves many Earth materials.
Water loses 80 calories of heat per gram when it freezes.
Water cools its surroundings when it evaporates.
Water expands when it freezes.
changing the position of crustal plates.
changing the Earth's prevailing wind patterns.
increasing the rate of chemical weathering.
increasing the amount of ozone in ground water.
depth of the water table.
steepness of hill slopes.
elevation of the surface.
type of bedrock material.
chemical weathering
deposition
erosion
physical weathering
chemical weathering
deposition
erosion
physical weathering
chemical weathering
deposition
erosion
physical weathering
its velocity increases
its velocity decreases
its velocity stays the same
its velocity increases
its velocity decreases
its velocity stays the same
its velocity increases
its velocity decreases
its velocity stays the same
its velocity increases
its velocity decreases
its velocity stays the same
erosion decreases and deposition increases
erosion decreases and deposition decreases
erosion increases and deposition increases
erosion increases and deposition decreases
the amount of sediment increases and the the maximum size that can be carried increases
the amount of sediment increases and the the maximum size that can be carried decreases
the amount of sediment decreases and the the maximum size that can be carried increases
the amount of sediment decreases and the the maximum size that can be carried decreases
A glacier is a large mass of ice that is floating in the very cold, northern oceans like the one that caused the Titanic to sink.
A glacier is a large mass of ice that moves over the Earth like a giant ice cube flowing over the map.
A glacier is a large mass of ice on land that is made up of snow and ice, but does not move.
A glacier is a large mass of ice that flows out from a central point in a very similar way to the movement of a river.
unsorted and unstratified.
unsorted and well stratified.
well sorted and unstratified.
well sorted and well stratified.
glacial ice.
gravity.
running water.
wind.