Chapter 6 Test Review
Instructions: Click on the button to see if your answer is correct or not. I recommend keeping track of how many you get correct on your first try. Then, divide by 65 and multiply by 100 to see what your grade would have been had this been the test. Also, watch your timing! These 65 questions should not take you longer than an hour.
It rises up from the Earth's surface.
It sinks towards the Earth's surface.
Pressure does not effect the direction that air moves.
Warm and Humid.
Warm and Arid.
Cool and Humid.
Cool and Arid.
It will increase.
It will decrease.
It will stay the same.
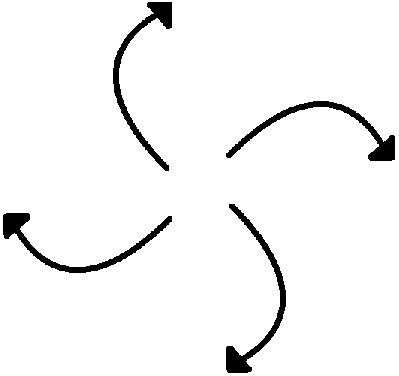
High pressure, and Northern Hemisphere
Low pressure, and Northern Hemisphere
High pressure, and Southern Hemisphere
Low pressure, and Southern Hemisphere
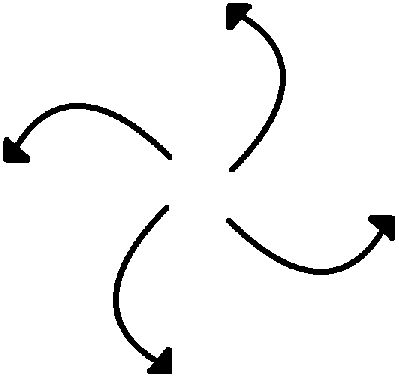
High pressure, and Northern Hemisphere
Low pressure, and Northern Hemisphere
High pressure, and Southern Hemisphere
Low pressure, and Southern Hemisphere
Clockwise, away from the center, and down towards the surface.
Clockwise, towards the center, and away from the surface (up).
Counterclockwise, away from the center, and down towards the surface
Counterclockwise, towards the center, and away from the surface (up).
Precipitation
Condensation
Evaporation
Infiltration
Precipitation
Condensation
Evaporation
Infiltration
What is evaporational cooling?
The cooling effect on the air as heat energy is released by water molecules as they condense from the surrounding air.
The cooling effect on the air as heat energy is released by water molecules as they evaporate from the surrounding air.
The cooling effect on the air as heat energy is absorbed by water molecules as they condense from the surrounding air.
The cooling effect on the air as heat energy is absorbed by water molecules as they evaporate from the surrounding air.
The air is saturated, heat energy is absorbed from the air, and there is a condensational surface.
The air is saturated, the air cools below dewpoint, and there is a condensational surface.
The air is unsaturated, heat energy is absorbed from the air, and there is a condensational surface.
The air is unsaturated, the air cools below dewpoint, and there is a condensational surface.
What is a cloud made up of?
Water vapor and a heat source
Water droplets or ice crystals around condensation nuclei
Water droplets or ice crystals and a heat source
Water vapor evaporating around condensation nuclei
What causes a cloud to look gray?
Water vapor is gray in color
Sunlight is absorbed by the water molecules so that they can condense
The thickness of the cloud blocks sunlight from passing through
The clouds are reflecting the color of the land
If the air temperature is 10°C, which of the following dewpoint would result in the highest probability of precipitation?
-4°C
0°C
6°C
8°C
The diagram below shows a sealed container holding liquid water and clean air saturated with water vapor (relative humidity is 100%). The container has been placed on a block of ice to cool the air.
Which statement best explains why a cloud has not formed in the sealed container?
The ice is cooling the water in the container.
The air in the container is above the freezing point.
The water in the container is still evaporating.
The air in the container lacks condensation nuclei.
Clouds usually form when moist air rises, because the air
expands and cools.
contracts and cools.
expands and warms.
contracts and warms.
What is the dewpoint if the dry bulb is 20°C and the wet bulb is 16°C?
4°C
9°C
14C
The value cannot be determined.
What is the relative humidity if the air temperature is 14°C and the wet bulb is 10°C?
6%
8%
54%
60%
In the diagram below, which two containers have the same relative humidity?
A and B
B and C
A and C
In the diagram below, which two containers have the same relative humidity?
A and B
B and C
A and C
What happens to the probability of precipitation as the relative humidity increases?
It increases
It decreases
It stays the same
What is the dewpoint if the dry bulb is 27°C and the wet bulb is 20°C?
7°C
16°C
54°C
It cannot be determined.
What is the relative humidity if the dry bulb temperature is 28°C and the dewpoint is 14°C?
9%
17%
19%
42%
What latitudes would have the highest amount of annual precipitation?
30°N, 30°S, 90°N, and 90°S
0°, 60°N, and 60°S
30°N, 30°S, 60°N, and 60°S
0°, 90°N, and 90°S
What are the three reasons for why the air over the Equator generally rises?
It is moist, warm, and has a low density.
It is dry, warm, and has a low density.
It is moist, cool, and has a low density.
It is dry, cool, and has a low density.
What are the main global winds called in our area, and how did they get that name?
The Prevailing Westerlies, because they move from west to east.
The Prevailing Easterlies, because they move from west to east.
The Prevailing Westerlies, because they move from east to west.
The Prevailing Easterlies, because they move from east to west.
Where are the Doldrums located?
At 0° latitude
At 30° latitude
At 60° latitude
At 90° latitude
What is a divergent air current?
Air currents that are coming together.
Air currents that are moving apart.
Air currents traveling in the same direction.
Air currents that are not moving.
If city A has a barometric pressure of 950.1 mb and city B has an air pressure of 1000.5 mb, which way would the winds move in this area?
From city A to city B
From city B to city A
Away from both cities
Towards both cities
What direction does wind always move?
Towards the water
Away from the surface
From high pressure to low pressure
From low pressure to high pressure
When isobars on a weather map are close together, what type of weather condition is most likely to be present in that area?
Clearing conditions
Strong, fast moving winds
Weak, slow moving breezes
An approaching storm
What will happen to the distance between the isobars on a weather map as wind velocity decreases?
The distance between isobars will increase.
The distance between isobars will decrease.
The distance between isobars will stay the same.
It is unpredictable.
On a clear, calm summer day, which way would you expect the winds to move at the beach, providing that the temperature of the water was the same as the temperature of the land at sunrise?
From the water to the land.
From the land to the water.
Over the land and water in the same parallel direction.
Over the land and water in a perpendicular direction.
When does a land breeze occur (Time of day and reason)?
At night, when the land cools faster than the water.
At night, when the water cools faster than the water.
During the day, when the land cools faster than the water.
During the day, when the water cools faster than the water.
What is a barometer?
An instrument that measures air temperature.
An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.
An instrument that measures wind speed.
An instrument that measures wind direction.
What is an anemometer?
An instrument that measures air temperature.
An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.
An instrument that measures wind speed.
An instrument that measures wind direction.
What is the difference between the dry bulb on a psychrometer and a thermometer?
The dry bulb measures evaporational cooling, whereas the thermometer measures the air temperature.
The dry bulb measures the air pressure, whereas the how hot it is out.
The dry bulb measures wind speed, whereas the the thermometer measures the air temperature.
Nothing, they are the same thing
What does a rapidly falling barometric pressure usually indicate?
Approaching storm conditions
clearing conditions
decreasing humidity
decreasing temperatures
When using a psychrometer, both the dry bulb and the wet bulb are used to find relative humidity and the dewpoint, but what does the dry bulb actually measure on its own?
Relative humidity
Dewpoint
Air temperature
Evaporational cooling
When using a psychrometer, both the dry bulb and the wet bulb are used to find relative humidity and the dewpoint, but what does the wet bulb actually measure on its own?
Relative humidity
Dewpoint
Air temperature
Evaporational cooling
How are winds named?
Where they are going to
Where they came from
The person who discovered them
The general compass direction where the wind is found.
What weather conditions are most likely to exist when the barometric pressure increases?
Cold, dry air and clearing skies
Warm, moist air and storm conditions
Cold, moist air and storm conditions
Warm, dry air and clearing conditions
In which layer can most of the water vapor in the atmosphere be found?
The Troposphere
The Stratosphere
The Mesosphere
The Thermosphere
Wind is caused mainly by air-pressure differences that result from
the absorption of ultraviolet radiation by Earth's landmass.
the uneven heating of Earth's atmosphere.
the rotation of Earth on its axis.
the radiation of heat from Earth's landmasses to water bodies.
What is another commonly used term for evaporation?
Condensation
Infiltration
Vaporization
Precipitation
In which zone of the atmosphere would a temperature of 85°C most likely be found?
The Troposphere
The Stratosphere
The Mesosphere
The Thermosphere
Condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere is most likely to occur when a condensation surface is available and
the air is saturated with water vapor.
the air pressure is rising.
a strong wind is blowing.
the temperature of the air is blow 0°C.
By which process are clouds, dew, and fog formed?
evaporation
condensation
melting
precipitation
Clouds usually form when
evaporation has warmed the surrounding air.
air temperature reaches the dewpoint.
condensation nuclei have been removed from the air.
relative humidity is 0%.
Clouds usually form when moist air rises, because the air
contracts and warms.
contracts and cools.
expands and warms.
expands and cools.
At which of these latitudes would average annual precipitation be the greatest?
0°C
30°C
60°C
90°C
The dewpoint changes most directly as a result of changes in the
pressure
wind direction
convection currents
water vapor contents
Rapidly falling barometric pressure readings usually indicate
decreasing humidity.
decreasing temperatures.
clearing conditions.
approaching storm conditions.
As a weather balloon released from the surface of the Earth rises through the troposphere, the instruments it carries will usually indicate that
temperatures increase, but atmospheric pressure and concentrations of water vapor decrease.
temperatures decrease, but atmospheric pressure and concentrations of water vapor decrease.
temperatures, atmospheric pressure and concentrations of water vapor decrease.
temperatures, atmospheric pressure and concentrations of water vapor increase.
The direction of the wind is most likely due to air moving from areas of
high air humidity to low air humidity.
low air humidity to high air humidity.
high air pressure to low air pressure.
low air pressure to high air pressure.
As the temperature of the atmosphere at a given location increases, the air pressure will most likely
decrease.
increase.
stay the same.
Which factor is most directly related to wind velocity?
cloud type
pressure gradient
dewpoint
relative humidity
A high-pressure center is generally characterized by
warm, dry weather.
warm, wet weather.
cool, dry weather.
cool, wet weather.
What is the dewpoint temperature if the dry bulb is 4°C and the wet bulb is 3°C?
-8°C
-4°C
1°C
0°C
What is the relative humidity if the dry bulb is 27°C and the wet bulb is 20°C?
51%
52%
53%
54%
What is the dewpoint temperature if the air temperature is 16°C and the wet bulb depression is 10°C?
-10°C
-5°C
4°C
10°C
What is the relative humidity if the dewpoint is 12°C and the dry bulb temperature is 20°C?
4%
19%
58%
11%
If the wet bulb temperature is 22°C and the relative humidity is 100%, what is the dry bulb temperature?
0°C
22°C
88°C
12°C
If the wet bulb and the dewpoint are both 8°C, what is the relative humidity?
0%
51%
88%
100%
Which of the following statements is not true?
When the air is saturated, the dewpoint temperature is the same as the wet bulb and the dry bulb temperatures.
The wet bulb measures the change in temperature caused by evaporational cooling.
When the air is saturated, it cannot hold any more water vapor, and this is why its relative humidity is 0%.
100% relative humidity means that no more water will be able to evaporate until the relative humidity changes.
Dewpoint is
The temperature at which the air is saturated.
The temperature at which water evaporates.
The temperature of the moisture in the air.
The temperature of the air at midnight.